Purine base and its final metabolite, uric acid, were separated using multi-mode column, Asahipak GS-320 HQ. Purine base is a general name for compounds (nucleotide, nucleoside, base) containing purine structure and found in most foods. Through metabolic pathways, purines are broken down to uric acid, when exceeded amount of uric acid is accumulated in body, it may cause gout.
For the analysis of purines in food, first, homogenized food is freeze-dried and then dissolved in 70 % H2O2. By this hydrolysis process neutralizes the purines into purine bases.
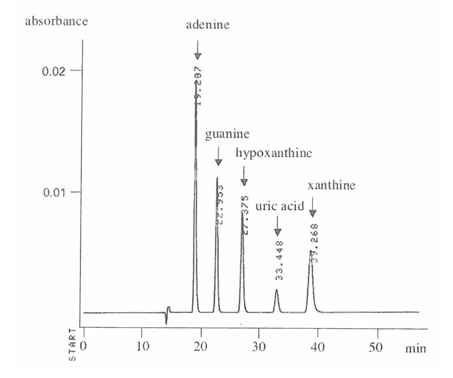
Sample : Purine base standards
Adenine
Guanine
Hypoxanthine
Uric acid
Xanthine
Column : Shodex Asahipak GS-320 HQ (7.5 mm I.D. x 300 mm) Eluent : 150 mM Sodium phosphate buffer (pH2.5) Flow rate : 0.6 mL/min Detector : UV (260 nm) Column temp. : 35 °C
Data provided by Prof. Kiyoko Kaneko, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Teikyo University
Sample Name Index
Operation Manual / Certificate of Analysis
Operation Manuals and Certificate of Analysis / Inspection Certificate for the following products can be downloaded here.
Product Name Index
Applications
- Nucleobases and Nucleosides (1) (DE-613)
- Nucleobases and Nucleosides (2) (NN-814)
- Nucleobases, Nucleosides and Nucleotides (GS-320 HQ)
- Nucleobases (1) (GS-320 HQ)
- Nucleobases (4) (DE-413)
- Guanine and Tryptophan (DM-614, NN-814 and DE-613)
- Adenosine and Derivatives
- "Umami" (GS-320 HQ)
- Nucleosides (1) (GS-320 HQ)
- Adenine Nucleotides in Red Blood Cell
- Purine Base in Beer (GS-320 HQ)
