SEC is a method which uses the principle that a larger molecular size(three dimensional
volume) sample elutes faster. In fact, the actual molecular size of the sample
is different according to the solvent in which the sample is dissolved. In the
case of polymers which have ionic functional groups, the ionic functional groups
repel each other and the apparent molecular size of the polymers becomes larger.
To prevent such ionic dissociation, the addition of salts such as NaNO3
or NaCl is known to be effective.
Especially, in the case of hydrophilic polymers, the existence of small amounts
of ionic functional groups affect the peak pattern and measurement results. Addition
of salts to the eluent is recommended even when it is considered that the sample
polymer have no ionic functional groups.
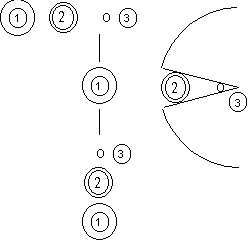
(Left): Principle of SEC
(Right, above): Large apparent size because
of repelling
(Right, below): Ordinary size
Applications
- Pullulan Standards (1) (SB-804 HQ)
- Pullulan Standards (2) (GF-310 HQ)
- Pullulan Standards (4) (Effects of Flow Rate) (SB-2002.5)
- Pullulan Standards (5) (Effects of Temperature) (SB-2002.5)
- Pullulan Standards (7) (GS-220 HQ)
- Pullulan Standards (9) (GF-7M HQ)
- Poly(Ethylene Oxide) and Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (SB-804 HQ)
- Dextran (1) (SB-805 HQ)
- Dextran (2) (DMSO Eluent) (KF-806M)
- Dextran (3) (SB-806M HQ)
- Polyacrylamide (1) (SB-805 HQ)
- Polyacrylamide (3) (Comparison with SB-807 HQ and SB-806 HQ)
- Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) (2) (Aqueous Eluent) (SB-806 HQ + SB-803 HQ)
- Sodium Polyacrylate (1) (SB-803 HQ + SB-802 HQ)
- Optimization of Mobile Phase for the Analysis of Sodium Polyacrylate (GF-7M HQ)
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone (3) (NaCl aq./CH3CN Eluent) (SB-806M HQ)
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone (6) (NaCl aq./CH3CN Eluent) (SB-806M HQ)
- Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) (1) (GF-510 HQ)
- Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) (2) (GF-7M HQ)
- Selection of Column (1) (Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate))
- Selection of Column (2) (Sodium Polyacrylate)
- Selection of Column (3) (Poly(Sodium Methacrylate))
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (6) (DE-613)
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (7) (SB-2002.5)
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (8) (SB-802.5 HQ)
- Sodium Dextran Sulfate (SB-806M HQ)
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (9) (GS-220 HQ)
- Influence of Column Temperature on Retention Time of PEG (GF-310 HQ and GS-320 HQ)
- Comparison of Chromatogram of PEG Mixtures
- Influence of Salt Concentration on Retention Time of PEG with GF-310 HQ Column
- Effects of Analysis of PEG Mixtures with GF-310 HQ by Composition of Eluent
- Effects of Analysis of PEG Mixtures with GS-320 HQ by Composition of Eluent
- Colominic Acid (SB-804 HQ)
- SEC Analysis of Latex Particles (KW405-4F)
- Poly(Sodium Methacrylate) (GF-7M HQ)
Applications (Related Information)
- Calibration Curves for SB-800 HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for SB-800 HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: PEG, PEO)
- Calibration Curves for SB-806M HQ (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan, PEG and PEO)
- Calibration Curve for SB-807 HQ (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for LB-800 Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for GF-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for GF-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: PEG, PEO)
- Calibration Curves for GS-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for GS-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: PEG, PEO)
- Calibration Curves of Hydrophilic Polymers (1) (Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate))
- Calibration Curves of Hydrophilic Polymers (2) (Sodium Polyacrylate)
- Calibration Curves of Hydrophilic Polymers (3) (Poly(Sodium Methacrylate))
