Sodium polyacrylate has many usages such as latex and food thickener, inorganic pigment dispersant, fabric sizing agent etc. Having carboxylic groups, a weak ionic functional group, sodium polyacrylate behaves as an ionic polymer. Often interactions other than size exclusion effect are observed for the SEC analysis of ionic polymers. When such interactions are present, the elution of the polymer may not be solely based on its molecular size. Therefore, it may interfere with an accurate molecular weight determination calculation of the polymer. Sodium polyacrylate of three different molecular weights were analyzed using Asahipak GF-7M HQ (an Aqueous/Organic (multi-solvent use) SEC column).
The effects of mobile phase pH on the analysis of sodium polyacrylate are summarized.
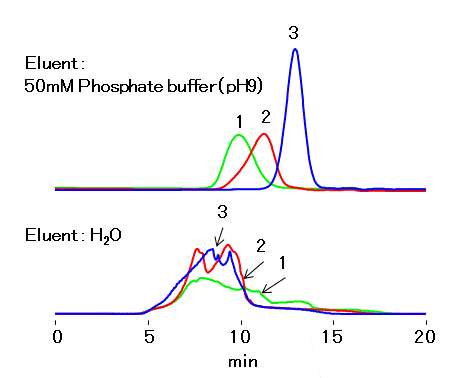
Water ---- Polymer exists as dissociated form (-COO-). Since the packing material of GF-7M HQ, polyvinyl alcohol, is slightly negatively charged, an ionic interaction (ion exclusion) between the polymer and the packing material occurs. This resulted in the elution of polymer as front.
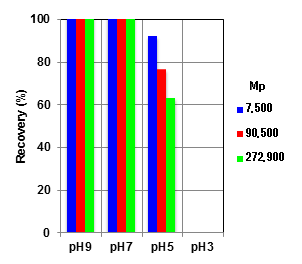
Mobile phase (pH 3) ---- polymer dominates in none dissociated form (-COOH). With this form, the low polarity of the polymer experiences hydrophobic interaction with the packing material. The polymer is adsorbed completely and will not elute from the column.
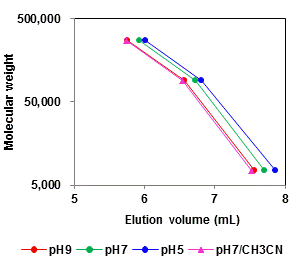
Mobile phase (pH 5) ---- Polymer dissociates in some level, and it exhibits as a mixture of -COO- and -COOH forms. The polarity of the polymer is higher than that at pH 3, however added salt in the mobile phase helps to suppress the ion exclusion effect. Although the presence of -COOH form causes hydrophobic interaction in addition to the size exclusion effect; this results in lowering of recovery rate and delay of elution. These phenomena are more substantial for the larger MW polymers.
Mobile phase (pH 7) ---- Polymer dissociates and -COO- form dominates. The higher polarity inhibits the hydrophobic interaction; less adsorption, appears as lesser delay in elution, is observed. Addition of ~10% acetonitrile can suppress the remaining hydrophobic interaction.
Mobile phase (pH 9) ---- No adsorption and delay in elution is observed since hydrophobic interaction is well suppressed as polymer is in fully dissociated form.
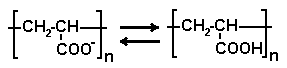
The pH of mobile phase is a key factor for the SEC analysis of ionic polymers as shown in this experiment. It is important to optimize the conditions for each ionic polymer since polarity and ionic strengths differ between polymers.
Sample :50 μL
Sodium polyacrylate 0.1 % each PSS-USA(Polymer Standards Service-USA)
| Mp | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. |
272,900
|
222,100
|
335,400
|
1.51
|
| 2. |
90,500
|
7,8400
|
131,200
|
1.67
|
| 3. |
7,500
|
6,200
|
8,300
|
1.34
|
Column : Shodex Asahipak GF-7M HQ (7.5 mm I.D. x 300 mm)
Eluent : H2O
50 mM Sodium phosphate buffer
50 mM Sodium phosphate buffer (pH7.0)/CH3CN=90/10
Flow rate : 0.6 mL/min
Detector : UV (210 nm)
Column temp. : 30 °C
Sample Name Index
Operation Manual / Certificate of Analysis
Operation Manuals and Certificate of Analysis / Inspection Certificate for the following products can be downloaded here.
Product Name Index
Applications
- Pullulan Standards (1) (SB-804 HQ)
- Pullulan Standards (2) (GF-310 HQ)
- Pullulan Standards (4) (Effects of Flow Rate) (SB-2002.5)
- Pullulan Standards (5) (Effects of Temperature) (SB-2002.5)
- Pullulan Standards (7) (GS-220 HQ)
- Pullulan Standards (9) (GF-7M HQ)
- Poly(Ethylene Oxide) and Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (SB-804 HQ)
- Dextran (1) (SB-805 HQ)
- Dextran (2) (DMSO Eluent) (KF-806M)
- Dextran (3) (SB-806M HQ)
- Polyacrylamide (1) (SB-805 HQ)
- Polyacrylamide (3) (Comparison with SB-807 HQ and SB-806 HQ)
- Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) (2) (Aqueous Eluent) (SB-806 HQ + SB-803 HQ)
- Sodium Polyacrylate (1) (SB-803 HQ + SB-802 HQ)
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone (3) (NaCl aq./CH3CN Eluent) (SB-806M HQ)
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone (6) (NaCl aq./CH3CN Eluent) (SB-806M HQ)
- Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) (1) (GF-510 HQ)
- Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) (2) (GF-7M HQ)
- Selection of Column (1) (Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate))
- Selection of Column (2) (Sodium Polyacrylate)
- Selection of Column (3) (Poly(Sodium Methacrylate))
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (6) (DE-613)
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (7) (SB-2002.5)
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (8) (SB-802.5 HQ)
- Sodium Dextran Sulfate (SB-806M HQ)
- Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Standards (9) (GS-220 HQ)
- Influence of Column Temperature on Retention Time of PEG (GF-310 HQ and GS-320 HQ)
- Comparison of Chromatogram of PEG Mixtures
- Influence of Salt Concentration on Retention Time of PEG with GF-310 HQ Column
- Effects of Analysis of PEG Mixtures with GF-310 HQ by Composition of Eluent
- Effects of Analysis of PEG Mixtures with GS-320 HQ by Composition of Eluent
- Colominic Acid (SB-804 HQ)
- SEC Analysis of Latex Particles (KW405-4F)
- Poly(Sodium Methacrylate) (GF-7M HQ)
Applications (Related Information)
- SEC Analysis of Ionic Sample
- Calibration Curves for SB-800 HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for SB-800 HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: PEG, PEO)
- Calibration Curves for SB-806M HQ (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan, PEG and PEO)
- Calibration Curve for SB-807 HQ (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for LB-800 Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for GF-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for GF-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: PEG, PEO)
- Calibration Curves for GS-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: Pullulan)
- Calibration Curves for GS-HQ Series (Aqueous Eluent: PEG, PEO)
- Calibration Curves of Hydrophilic Polymers (1) (Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate))
- Calibration Curves of Hydrophilic Polymers (2) (Sodium Polyacrylate)
- Calibration Curves of Hydrophilic Polymers (3) (Poly(Sodium Methacrylate))
