In this application, we compared Asahipak GS-220 HQ and SUGAR KS-802 for the analysis of low-molecular-weight water soluble dietary fibers. The analysis requires to divide the sample components into two fractions and calculate their ratios. One fraction includes hard-to-digest saccharides with their sizes larger than trisaccharide (hard to digest oligo saccharides and dietary fibers). The other fraction includes monosaccharides, disaccharides, and sugar alcohols. When using the GS-220 HQ, which works under size exclusion mode, the fraction of hard-to-digest components elutes before the allow mark in the figure and the other fraction elutes after the allow mark. Thus, the separation of the two fractions are easily obtained. Meanwhile, the KS-802 works under ligand exchange mode in addition to the size exclusion mode. This provides good separations of monosaccharides and disaccharides. On the other hand, this complex separation capability makes it difficult to simply separate the two fractions. Therefore, GS-220 HQ is more suitable for the fractional quantification of the low-molecular-weight water soluble dietary fibers than KS-802.
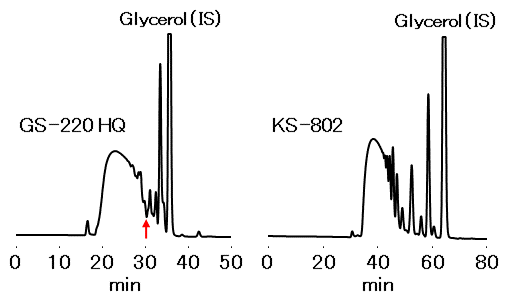
Sample : 20 µL
Low-molecular-weight water soluble dietary fiber
Columns : Shodex Asahipak GS-220 HQ Shodex SUGAR KS-802
(7.5 mm I.D. x 300 mm) x 2 (8.0 mm I.D. x 300 mm) x 2
Eluent : H2O H2O
Flow rate : 0.5 mL/min 0.3 mL/min
Detector : RI RI
Column temp. : 60 °C 80 °C
Sample Name Index
Operation Manual / Certificate of Analysis
Operation Manuals and Certificate of Analysis / Inspection Certificate for the following products can be downloaded here.
Product Name Index
Applications
- Hydrolyzed Dextran (2) (KS-802)
- Hydrolyzed Dextran (3) (NH2P-50 4E)
- Hydrolyzed Dextran (5) (KS-802)
- Hydrolyzed Dextran (6) (VN-50 4D)
- Hydrolyzed Dextran (7) (VN-50 4D by Gradient Elution)
- Isomaltooligosaccharides (NH2P-50 4E)
- Isomaltooligosaccharides (2) (VG-50 4E)
- Maltooligosaccharides (NH2P-50)
- Maltooligosaccharides (2) (VG-50 4E)
- Comparison of maltooligosaccharides separation
- N-Acetylchitooligosaccharides (1) (NH2P-50 4E)
- N-Acetylchitooligosaccharides (2) (VN-50 4D)
- Chitosan-Oligosaccharides (Chitooligosaccharides) (1) (NH2P-50 4E)
- Chitosan-Oligosaccharides (Chitooligosaccharides) (2) (Asahipak NH2P-50 4E)
- Chitosan-Oligosaccharides (Chitooligosaccharides) (3) (VN-50 4D)
- Cyclodextrins (Comparison of GS-220 HQ and KS-802)
- Analysis of Cyclodextrins (NH2P-50 4E)
- Analysis of Cyclodextrins According to Japan's Specifications and Standards for Food Additives Method (KS-802)
- Short-Chain Amylose (1) (NH2P-50 10E)
- Short-Chain Amylose (2) (ODP-50 6D)
- Hydrolyzed Starch (2) (KS-802)
- Sweetener (KS-802)
- Effects of Flow Rate (SC1211)
- Fructooligosaccharide Syrup (NH2P-50 4E)
- Analysis of Fructooligosaccharide Components (KS-802 + KS-801)
- Analysis of Fructooligosaccharides in Accordance to the Food System for Specified Health Use (VG-50 4E)
- Starch Syrup
- Xylooligosaccharides (1) (KS-801)
- Xylooligosaccharides (2) (VN-50 4D)
- Xylooligosaccharides (3) (SH1011)
- Degradation Product of Cellulose with Cellulase (PcCel45A) Digestion
- Oligosaccharide in Soy Bean (KS-802 + KS-801)
- Analysis of Trisaccharides (1) (NH2P-40 3E)
- Analysis of Trisaccharides (2) (VG-50 4E)
- Galactooligosaccharides (1) (VG-50 4E)
- Galactooligosaccharides (2) (KS-801, NH2P-50 4E)
- Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (SB-802.5 HQ)
- Analysis of Maltodextrin (VN-50 4D)
- Separation of Kestose and Maltose (KS-802)
